Detection of Covid-19 virus: Real Time RT-PCR
Some might be wondering how do doctors or medical officers detect the Covid-19 virus? What kind of sample test do they run in hospitals to determine the presence of the virus. Please note that this is just the overall idea or explanation of how the technique is used to detect the virus.
The test that is mainly used to detect Covid-19 virus is a technique or analysis called Real-Time Reverse-Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR). RT-PRC is a technique to detect the presence of a genetic component either it is a double stranded DNA in humans or a single stranded RNA that is usually in viruses and the coronavirus that is the cause of Covid-19 is single stranded RNA. What is interesting about RT-PCR is that it can determine the specific fragments of the specific coronavirus for Covid-19. Please be reminded that Covid-19 is the name of the disease that is caused by a coronavirus. Coronavirus has also caused other diseases such as SARS and MERS. So how does RT-PCR detects specifically the virus for Covid-19?
Firstly, the sample collection. Health workers will collects the samples from the nostrils or throat of the suspected patients. The sample then will be placed in a container in a cold condition so it can be transported to the laboratories or hospitals. In the labs, there is a health worker or to be more specific, medical laboratory technologist (MLT) or science officer. They are the ones who will analyse and process the samples that were taken. Then the RNA is extracted from the collected sample. The extracted RNA will then undergo the process of reverse transcription where the RNA will be turned into a double stranded complimentary DNA. After that, the extracted sample is inserted into a machine called thermal cycler. Thermal cycler can increase or decrease the temperature in a short amount of time that is important for RT-PCR.

So RT-PCR has 3 main steps. The first step, denaturation. At the temperature of 90-95℃, the double stranded cDNA will denature from two single strands of DNA due to the hydrogen bond breaking. The cycler will then lower the temperature to 50-55℃. This is when the second step comes in.
The second step called annealing is where a component called primer will attach to the target DNA or a specific fragment particularly of the coronavirus of Covid-19 on each strand. If the the virus was absent, the primer will not attach to the the two DNA strands. There are two primers that are Forward primer and Reverse primer. So let's say the Covid-19 virus is present. Both primers will attach itself to each single DNA strand by forming hydrogen bonds with ends of target sequence.
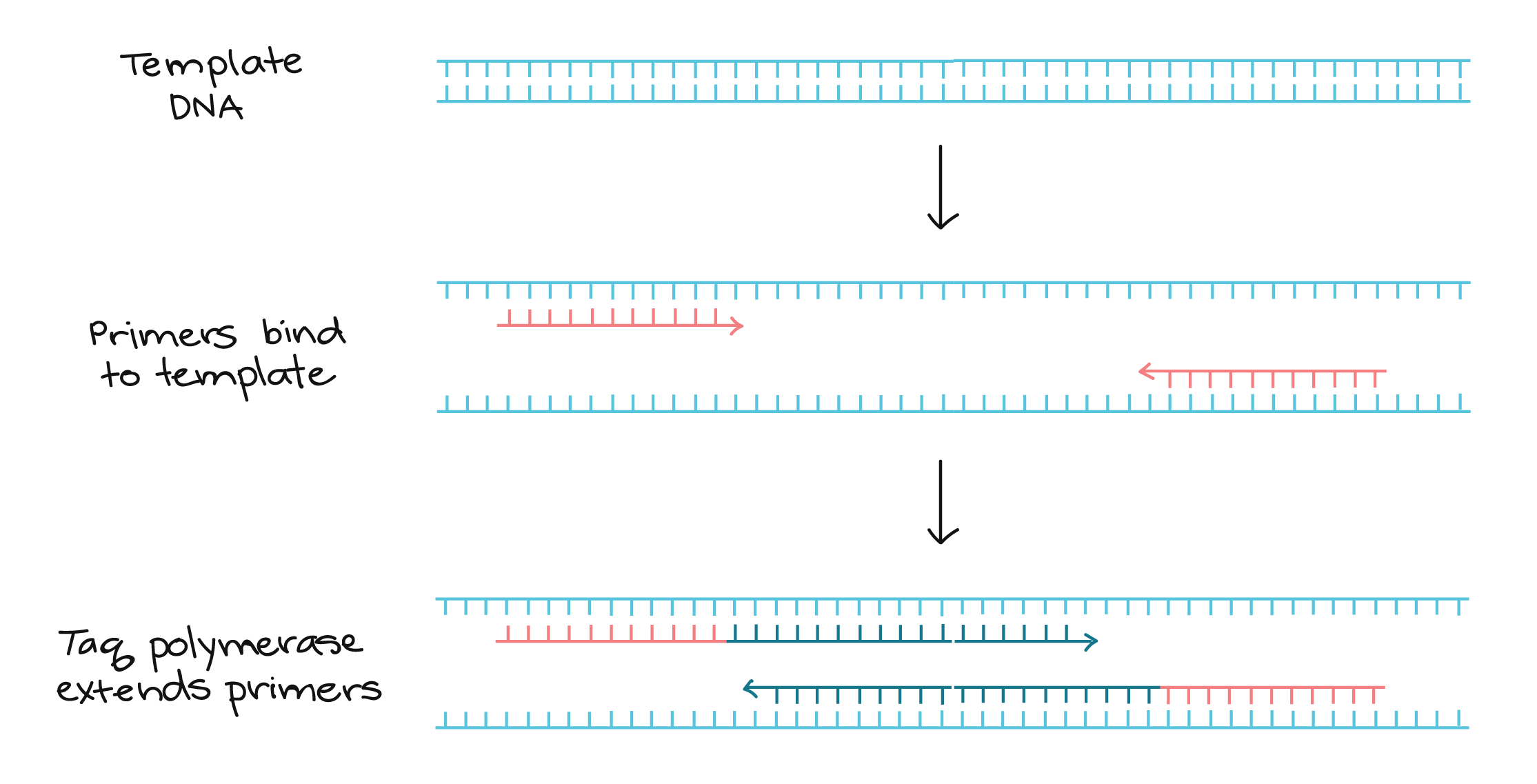
The the cycler will increase the temperature to 72℃. This will allow an enzyme called taq DNA polymerase to replicate the single DNA strands. The reason why we use taq DNA polymerase instead of normal DNA polymerase is because normal DNA polymerase in not heat stable such as taq DNA and will denature easily when exposed to high temperature. This step is called extension. At the end of the first cycle, there will be two new DNA strands identical to the original target. There will be up to 30-40 cycles to amplify the target DNA sequence. PCR can generate 100 billion similar molecules in 2 hours.

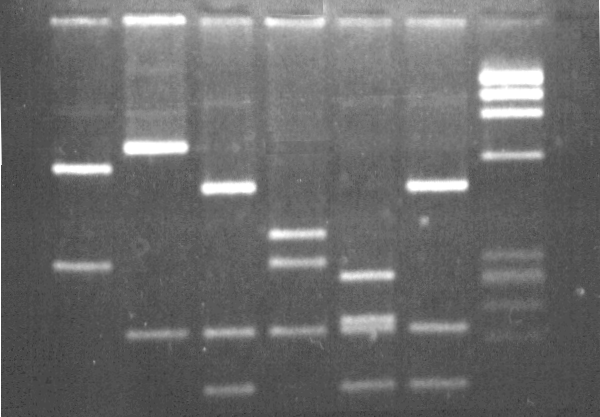
At the end of a PCR reaction, there is A LOT more of the Covid-19 virus DNA than before the reaction started. Now the sample is large enough to be seen on a gel and analysed. The analysis of PCR products is usually using gel electrophoresis.
For quantitative analysis, there is also a technique called Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) where a qPCR machine and a fluorescent dye in the PCR reaction (Sybr green or Taqman Probe) that bind to the amplified gene product and gives a Ct value , which later on gives an idea about the quantity or the RNA or DNA in the reaction depending on a standards used , in this case there is no need to do gel electrophoresis to see the amplified PCR product.
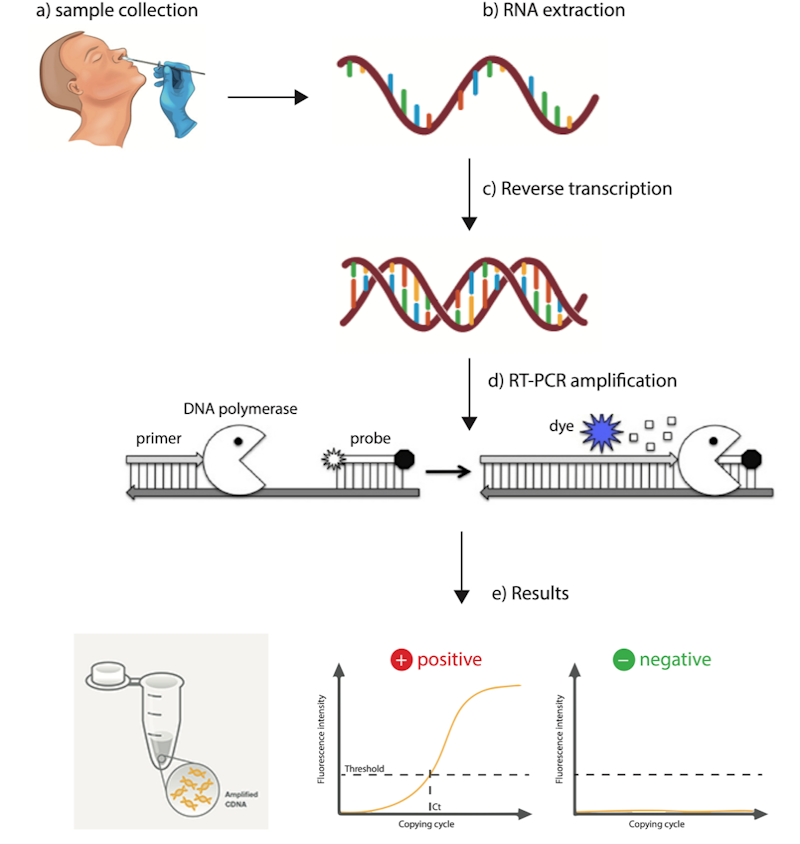
How long does this process takes? So this process takes 3-5 hours excluding the sample collection from patients and transportation of the samples. We should thank our brave front liners who risked their lives to battle the virus during this pandemic. Remember to constantly wash and sanitize your hands. Close your mouth and nose if you need to sneeze or cough. Keep your distance with other people and avoid going to crowded places. Stay safe everyone!
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Q&A on Coronaviruses (COVID-19). World Health Organization (WHO). 2020.
- Shen M, Zhou Y, Ye J, Abdullah AL-maskri AA, Kang Y, Zeng S, Cai S. Recent advances and perspectives of nucleic acid detection for coronavirus. J Pharm Anal. 2020;(xxxx). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2020.02.010
- Ministry of Health Malaysia. Guidelines COVID-19 Management in Malaysia No.5/2020. 2020.
- Chu DKW, Pan Y, Cheng SMS, Hui KPY, Krishnan P, Liu Y, Ng DYM, Wan CKC, Yang P, Wang Q, Peiris M, Poon LLM. Molecular Diagnosis of a Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Causing an Outbreak of Pneumonia. Clin Chem. 202
- Burd EM. Validation of laboratory-developed molecular assays for infectious diseases. Clin Microbiol Rev [No date]. 2010;23(3):550–76.

Comments
Post a Comment